Pew Report Illustrates Impact of Digital Technologies on Student Writing
July 16, 2013 (Washington D.C.) — A survey of teachers who instruct American middle and high school students finds that digital technologies are impacting student writing in myriad ways and there are significant advantages from tech-based learning.
Some 78% of the 2,462 advanced placement (AP) and National Writing Project (NWP) teachers surveyed by the Pew Research Center’s Internet & American Life Project say digital tools such as the internet, social media, and cell phones “encourage student creativity and personal expression.” In addition:
- 96% agree digital technologies “allow students to share their work with a wider and more varied audience”
- 79% agree that these tools “encourage greater collaboration among students”
According to teachers, students’ exposure to a broader audience for their work and more feedback from peers encourages greater student investment in what they write and in the writing process as a whole.
At the same time, these teachers give their students modest marks when it comes to writing and highlight some areas needing attention. Asked to assess their students’ performance on nine specific writing skills, teachers tended to rate their students “good” or “fair” as opposed to “excellent” or “very good.” Students received the best ratings on their ability to “effectively organize and structure writing assignments” and their ability to “understand and consider multiple viewpoints on a particular topic or issue.” Teachers gave students the lowest ratings when it comes to “navigating issues of fair use and copyright in composition” and “reading and digesting long or complicated texts.”
These findings emerge from an online survey conducted by the Pew Research Center’s Internet & American Life Project in collaboration with the College Board and the National Writing Project. It is a non-probability sample of 2,462 middle and high school teachers currently teaching in the U.S. and its territories, conducted between March 7 and April 23, 2012. Some 1,750 of the teachers are drawn from a sample of advanced placement (AP) high school teachers, while the remaining 712 are from a sample of National Writing Project teachers.
“These results challenge in many ways the notion that students’ writing skills are being undermined by their increasing engagement with digital tools and platforms,” notes Kristen Purcell, Associate Director for Research at the Pew Internet Project. “Teachers do have concerns that digital tools are blurring the lines between formal and informal writing and see writing skills that need improvement, but they also see the benefit of students having more people respond to their writing and the increased opportunities for expression these digital tools offer.”
Half (50%) of these teachers say digital tools make it easier to teach writing, with just 18% saying digital tools make the process more difficult. In particular, teachers value interactive platforms which allow them to work alongside a student on a piece of writing, and allow students to edit and view one anothers’ work. Among this group of teachers:
- 52% say they or their students use interactive whiteboards in their classes
- 40% have students share their work on wikis, websites or blogs
- 36% have students edit or revise their own work and 29% have students edit others’ work using collaborative web-based tools such as GoogleDocs
At the same time, teachers expressed concerns about the “creep” of informal grammar and style into “formal” writing, as well as students’ impatience with the writing process and their difficulty navigating the complex issues of plagiarism, citation and fair use. Specifically:
- 68% of these teachers say digital tools make students more likely—as opposed to less likely or having no impact—to take shortcuts and not put effort into their writing
- 46% say these tools make students more likely to “write too fast and be careless”
- Just 8% describe their students as “excellent” or “very good” when it comes to navigating issues of fair use and copyright in composition — 30% give their students the lowest rating of “poor”
- Just 15% rate students as “excellent” or “very good” when it comes to appropriately citing content, with the majority rating students “fair” (37%) or “poor” (20%) in this area
Reflecting these latter concerns, a majority of these teachers spend class time “discussing with students the concepts of citation and plagiarism” (88%) and “discussing with students the concepts of fair use and copyright” (75%).
While the survey includes teachers of all subjects, English/Language Arts teachers in the sample consistently express more positive views of the impact of digital tools on student writing and the potential of these tools to help them teach writing. Almost two-thirds (64%) of English/Language Arts teachers surveyed say digital tools make teaching writing easier, compared with 32% of Math teachers, 38% of Science teachers, and 45% of History/Social Studies teachers. English teachers are the most likely to use collaborative online platforms with their students, and are more likely than teachers of other subjects to say digital tools increase the likelihood students will revise and edit their work. They are the least likely of all teachers to say digital tools make students careless in their writing or undermine grammatical and spelling skills.
“Teachers, writing teachers especially, do not view good writing and the use of digital tools as being at war with each other,” added Judy Buchanan, Deputy Director of the National Writing Project and a co-author of the report. “When educators have opportunities to integrate new technologies into teaching and learning, they are the most optimistic about the impact of digital tools on student writing and their value in teaching the art of writing. They gave countless examples of the creative ways they use emerging digital tools to impart writing skills to today’s students.”
When it comes to writing skills, here is how these teachers rate their students:
Teachers most likely to rate students’ specific writing skills as “good” or “fair”
Overall, how would you rate your students in their ability to do each of the following?
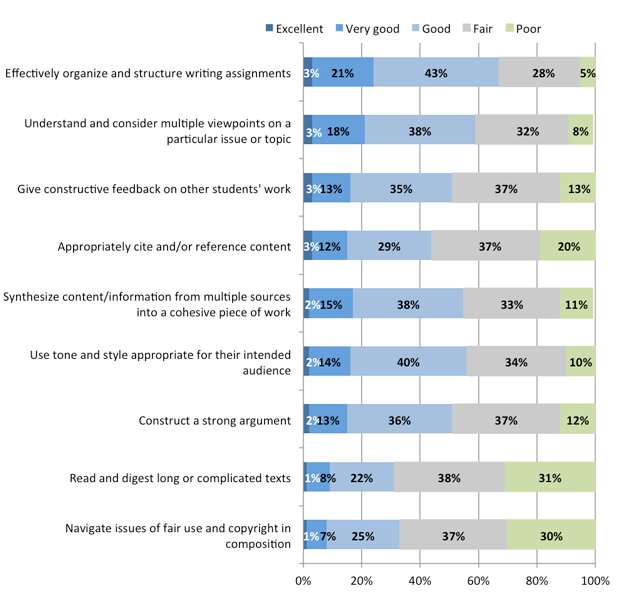
Source: The Pew Research Center’s Internet & American Life Project Online Survey of Teachers, March 7 to April 23, 2012. Based on a non-representative sample of 2,067 middle and high school teachers.


